Scalable computing resources are becoming more and more popular each day. Various professionals look for efficient ways to manage heavy tasks.
With such demand, you need a transformative solution for resource management. This is where Infrastructure as a service (IaaS) comes in. Let’s see what IaaS is and the range of products and services it offers.
What is Infrastructure as a Service?
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) represents a significant shift in resource handling. Traditionally, entities relied on physical infrastructure, which tied up funds and limited adaptability. IaaS revolutionizes this by providing virtualized online servers, storage, and networking control resources.
IaaS functions on a pay-as-you-go system, appealing to projects of any size. Whether you’re a solo 3D artist tackling a complex rendering project or a machine learning expert training advanced models, IaaS provides the necessary processing power and storage capacity at the right time. Through cloud providers, users can easily adjust their infrastructure size, ensuring payment only for utilized resources.
The shortest definition would be Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), a cloud computing service that provides virtualized computing resources over the internet.
IAAS Explained: How Does It Work
The power of IaaS is its capacity to abstract computing infrastructure, offering it as a service accessible remotely. Virtualization tech makes this possible, enabling cloud providers to create VMs on physical servers. These VMs can be customized with CPU, memory, and storage based on user needs.
Users who register for an IaaS platform rent part of the cloud service provider’s data center. This covers computing resources and essential infrastructure like cooling systems and security measures. Users access virtualized resources via a web interface or API to deploy, manage, and monitor applications.
One benefit of implementing IaaS is its scalability, allowing users to add resources for demand spikes. This flexibility is valuable for apps with changing workloads, like customer websites. Additionally, IaaS providers offer extra services like backups, recovery, and monitoring for reliability and security.

Types of IAAS Products
IaaS is not a one-size-fits-all solution; rather, it encompasses a wide range of products designed to meet the diverse needs of its users.
The most common types of IaaS products include:
- Virtual Machines (VMs): The backbone of IaaS, Virtual Machines (VMs) are virtual servers that can be customized with specific operating systems, processing power, memory, and storage resources. They provide the computational horsepower required for running applications and processing large volumes of data.
- Storage Solutions: IaaS platforms offer various storage options, including block storage for high-performance requirements, file storage for shared access, and object storage for scalable, unstructured data. These solutions ensure that users have the flexibility to store and manage their data efficiently, regardless of its type or volume.
- Networking Capabilities: Networking resources, such as virtual private networks (VPNs), load balancers, and firewalls, are integral components of IaaS offerings. They enable secure, high-speed connectivity between the virtualized resources and the wider internet, facilitating the smooth operation of hosted applications and services.
Professionals in fields needing heavy computing tasks must grasp available IaaS products. Rendering 3D models, running simulations, or training algorithms requires selecting storage and networking wisely.
Infrastructure as a Service provides a flexible, adaptable, and economical way to handle computing resources. Offering virtualized infrastructure instantly, IaaS allows professionals to scale projects efficiently. Exploring different IaaS models, like its cloud applications and provider selection criteria, shows its importance in the future of digital innovation.
Infrastructure as a Service Use Cases
The versatility of IaaS makes it an invaluable resource across various sectors that implement IaaS. By providing virtualized computing resources, IaaS allows businesses to expand and adjust operations easily. This adaptability is especially useful for development environments, where teams can swiftly adjust virtual machine capacity, cutting down on managing in-house data centers.
IaaS is the foundation for cloud-native apps, enabling devs to utilize cloud providers for computing, storage, and networking. This setup enables the development of reliable and scalable apps without requiring extensive infrastructure handling. For example, IaaS suppliers provide object storage solutions for managing vast amounts of unstructured data, like images and videos, frequently utilized by 3D artists and product renderings.
Another vital application of IaaS is hosting customer-facing websites, ensuring operational and responsive services under heavy traffic. This reliability is crucial for uninterrupted user services. Cloud render providers use IaaS to offer specialized rendering services to 3D designers and animation studios, enabling efficient rendering of complex projects.
Speeding up Development Cycles
One benefit of IaaS is speeding up development cycles and offering quick resource access. This agility is especially useful for cloud app teams, boosting productivity and innovation. The use of IaaS also promotes a more iterative and responsive development environment.
Teams can leverage additional services IAAS platforms offer, such as automated scaling and performance monitoring, to optimize their application code in real-time. This dynamic approach to development speeds up the release cycles. It ensures that the applications are optimized for performance and cost.
IaaS provides a significant benefit for deploying app code, letting developers focus on core development. Adding infrastructure services to your business model helps you deploy new apps quickly without upfront hardware investments.
Ensuring Business Reliability
Reliability is important for business operations, and IaaS is important in ensuring that organizations can deliver their services consistently. By using cloud services, businesses can attain redundancy and fault tolerance that is not affordable with on-premises data centers. The IaaS infrastructure, overseen by cloud providers, is safeguarding your assets and guarantees high availability and disaster recovery, preventing data loss and downtime.
IaaS provides strong networking resources like VPNs and firewalls, boosting data transmission security. This holistic security strategy is vital for safeguarding sensitive data and retaining client trust. Moreover, IaaS scalability enables managing extensive data and traffic loads while maintaining performance, ensuring accessible, efficient customer websites and apps.
Mastering Cloud Finances
Managing cloud finances requires understanding various cost models. Monitoring usage is essential to avoid unexpected expenses. Companies often overlook the importance of forecasting in cloud budgeting. Accurate predictions can significantly reduce costs. Tools and services are available to help manage cloud finances effectively.
They provide insights into spending patterns and potential savings. Different cost models include pay-as-you-go and reserved instances. Each has its benefits and challenges. Regularly checking usage helps identify wasteful spending. Forecasting helps in allocating budgets more efficiently. It involves analyzing past usage trends.
Cloud finance management tools offer detailed reports and analytics and suggest areas for cost optimization. Understanding these aspects is crucial for financial efficiency in the cloud.
Choosing the Right IAAS Provider
When choosing an IAAS provider, consider your needs, provider capabilities, reliability, scalability, security, support, and cost. For instance, MaxCloudON’s dedicated cloud hosting offers scalable solutions tailored to professionals like 3D rendering and machine learning. If you need specialized resources such as GPUs for machine learning or complex computations, check out MaxCloudON’s cloud GPU servers, equipped with dedicated graphics and processing power.
Furthermore, the provider must match your project’s needs for storage, networking, and extra services like backups and monitoring. They must be able to back cloud-native apps and provide scalable computing resources.
Assessing the provider’s ability to grow with your business is essential. Look for flexible plans that allow for adjustments. Ensure the provider’s security measures meet industry standards to protect your data. Customer support quality can greatly impact your experience.
Choose a provider with a strong reputation for reliable and accessible support. Compare costs carefully, considering both short-term and long-term expenses. A provider’s global presence can affect performance and compliance. Select one that aligns with your geographical needs.
The Future of IAAS
Infrastructure as a Service is always changing and influenced by new technologies and trends. Artificial intelligence and machine learning are incorporated into IAAS platforms to streamline infrastructure management, enhancing efficiency and cost-effectiveness. The increasing focus on sustainability is compelling cloud providers to embrace eco-friendly practices and minimize the environmental footprint of cloud computing.
Advances in virtualization and networking will provide more flexibility for businesses using IAAS. The future of IAAS ensures improved cloud services for innovative cloud-native applications.
Frequently Asked Questions:
-
What are IaaS and examples?
IaaS, or Infrastructure as a Service, provides high-level APIs used to abstract various details of underlying network infrastructure like physical computing resources. Examples include Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud Platform (GCP), and Microsoft Azure.
-
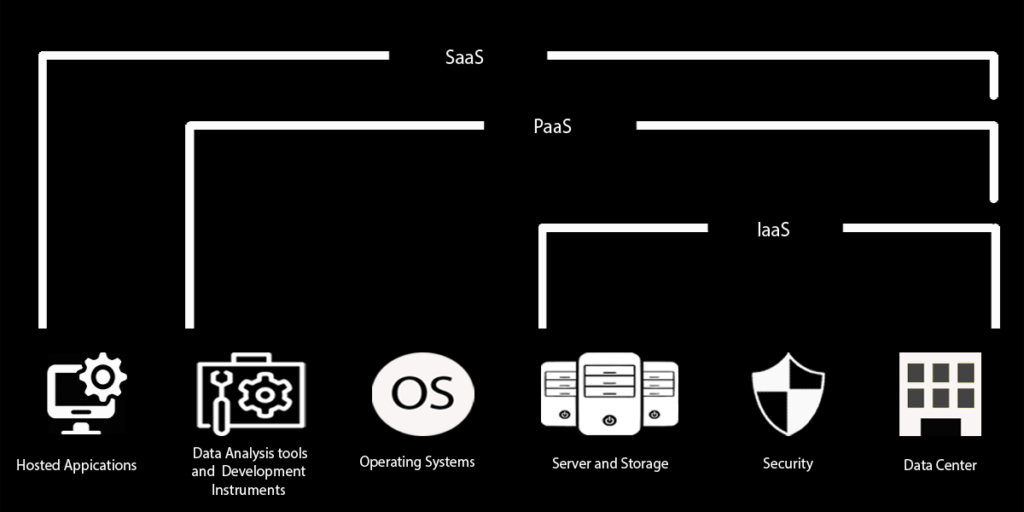
What is the difference between IaaS and PaaS?
IaaS provides the raw computing resources for use over the internet, such as virtual machines and storage, while PaaS offers a platform allowing customers to develop, run, and manage applications without managing the underlying infrastructure.
-
How does IaaS work?
IaaS works by providing virtualized computing resources through a cloud provider. Users can rent virtual machines, storage, and other infrastructure components on a pay-as-you-go basis, offering flexibility and scalability for various computing tasks.
-
What are the four types of cloud computing?
The four main types of cloud computing are Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), Software as a Service (SaaS), and Function as a Service (FaaS), each providing different levels of control and management over computing resources.