The advancements in internet technology and the development of cloud computing platforms enabled software to be accessed remotely. They are used over the internet without the need for powerful local hardware.
A leading role in this change is Software as a Service (SaaS), which has streamlined software delivery and redefined the relationship between providers and users. SaaS is now essential for numerous business operations, providing unmatched flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness.
As a concept, Software as a Service represents a shift from the conventional software ownership model. Instead of buying and setting up software on separate devices, SaaS provides online access to software through web browsers or specific SaaS apps.
This model aligns with cloud computing, where remote data centers manage data and applications. The SaaS model simplifies software management and offers benefits, ensuring you access the latest features and updates.
What is Software as a Service (SaaS)?
In short, Software as a service or SaaS, is a distribution model that allows you to access software applications over the internet. Most SaaS providers typically do this on a period subscription basis.
This model differs from the traditional approach of purchasing software licenses and handling applications on-site. SaaS is a critical component of cloud computing services, offering a range of applications from customer relationship management to enterprise resource planning and beyond.
The essence of the SaaS model lies in its delivery method. SaaS providers host applications on remote servers and are responsible for maintenance, updates, and security. You reach the app software through an internet connection, usually with only a web browser.
This eliminates the need for complex infrastructure management and reduces the burden on internal IT resources. One of the defining features of SaaS is its subscription-based pricing structure. Unlike the traditional model of buying upfront software, SaaS works on a pay-as-you-go basis, where users pay a recurring fee for access to the software. This model provides various benefits, like reduced upfront expenses, adjusting subscriptions based on demand, and stopping services if necessary.
SaaS Core Concept
The main idea of SaaS is to provide applications on an online hosted platform, with the cloud provider managing infrastructure like servers and storage. This centralization of services enables a consistent and updated experience for all users.
Let’s see its characteristics in detail below:
- Multi-tenancy: A fundamental aspect of the SaaS model is multi-tenancy. This design enables numerous clients to utilize one application instance, maintaining data security and separation. Multi-tenancy boosts resource use and efficiency for the “SaaS provider,” leading to lower user expenses.
- Scalability: The SaaS scalability enables you to adjust your usage and subscription levels based on your current needs. This benefits industries with fluctuating workloads, like animation studios that need extra computing power for rendering.
- Accessibility: Accessibility is also a core characteristic of SaaS. You can access SaaS applications from any device with an internet connection, providing flexibility and mobility, essential in today’s fast-paced business environment.
- Reliability: Reliability is very important, as you expect the service to be available around the clock with minimal downtime. SaaS companies invest in robust cloud infrastructure and data centers to ensure client business continuity.
- Security: Security is another critical feature of a successful SaaS offering. With the increasing prevalence of cyber threats, application vendors must implement comprehensive cloud security measures to protect sensitive customer data. This involves using advanced encryption, frequent security audits, and following industry standards to ensure trust.
- Customization and integration: Customization and integration capabilities are also essential for a SaaS offering to succeed. Businesses frequently work with various applications, and a SaaS solution should integrate with them seamlessly. The smooth integration through robust application programming interfaces (APIs) and development tools allows for customization and extension of the SaaS application’s functionality.
- Support: Customer support is vital for a successful SaaS solution, with documentation, responsive support, and troubleshooting resources being essential for your satisfaction. As SaaS solutions develop, vendor support becomes a key differentiator in the market.
Software as a Service is a model that has redefined the software industry. SaaS offers many benefits that fulfill the needs of contemporary businesses and professionals, particularly in challenging areas like animation, architecture, and machine learning.
The flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness attract people and organizations aiming to optimize software investments and remain competitive in the digital landscape.
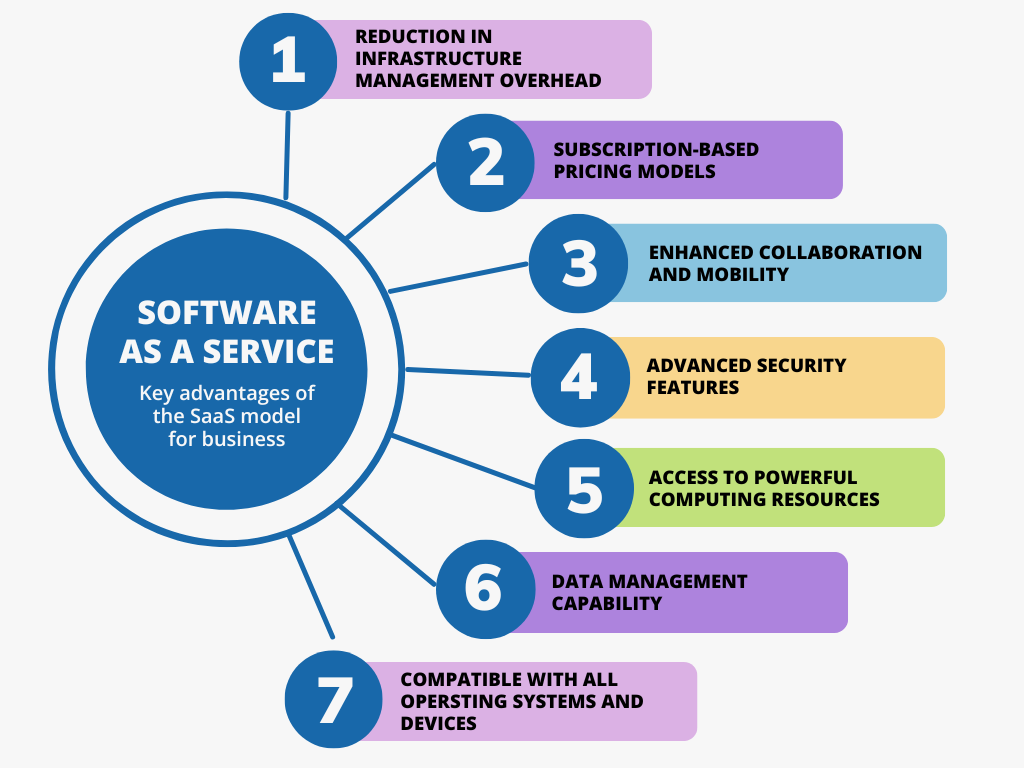
Advantages of SaaS for Business
The SaaS model has become a game-changer for businesses across various industries. Its advantages extend beyond the simplicity of web-based software access and include benefits that align with the strategic goals of modern organizations.
From cloud services offering data storage to SaaS apps improving business software, the SaaS model boosts corporate efficiency.
Infrastructure optimization
One benefit of SaaS is the decrease in infrastructure management burden. Businesses no longer require investing in data centers or computing resources. Instead, the cloud provider handles all aspects of the cloud computing infrastructure, allowing you to concentrate on your core tasks.
This change from on-premises software to SaaS reduced energy expenses and environmental impact, supporting sustainability in business practices.
Predictable costs
Another significant advantage is the subscription-based pricing models that many SaaS providers offer. This method helps companies forecast software costs accurately and avoid significant initial expenses linked to conventional software investments and operational costs.
The subscription model also provides the flexibility to scale up or down based on current needs, which is particularly advantageous for businesses with fluctuating demands.
Collaboration
SaaS solutions also promote enhanced collaboration and mobility. Teams collaborate in real-time using web-based apps from any location with internet access, breaking geographical barriers.
This collaboration has been crucial given the rising trend toward remote work and global teams.
Security
SaaS vendors often provide advanced security features that might be out of reach for individual businesses. By leveraging economies of scale, SaaS companies can invest in additional cloud security measures such as frequent updates and robust encryption.
The strict security protocols ensure your data is safe, crucial for maintaining trust and meeting legal obligations.
Powerful computing resources
SaaS options provide access to powerful computing resources and platforms without requiring hardware investments. This access to powerful software tools enables smaller firms and independent professionals to compete with larger organizations.
It is highly beneficial for industries that rely on advanced software such as 3D rendering or machine learning.
Data management
SaaS applications often come with built-in analytics and reporting tools, providing businesses valuable insights into their operations.
This data management capability allows for data-driven decision-making and a better understanding of customer behavior and business performance.
Compatibility
Lastly, SaaS solutions are typically compatible with all operating systems and devices, ensuring a consistent experience regardless of the hardware.
This compatibility is crucial in today’s varied tech environment and eases the load on IT teams handling various software versions.
From saving costs to enhancing security and collaboration, SaaS empowers companies to succeed in the digital age. With the continuing growth of the SaaS market, we can expect these benefits to become even more pronounced, establishing SaaS as a cornerstone of modern business technology.
Industry-Specific SaaS Applications
The versatility of SaaS extends to its ability to cater to various industry-specific needs. SaaS applications are customized to address specific industry challenges, offering diverse tools – from CRM systems helping sales teams to ERP systems integrating operations.
Below, we will review them in more detail.

Architecture and Design
SaaS solutions provide powerful tools for architectural rendering of 3D models, images, and simulations. These platforms often include data storage capabilities, allowing you to save large design files and access them from anywhere.
For 3D artists and graphic designers, this means the ability to collaborate on projects without transferring large files back and forth, streamlining the design process.
Machine Learning
For machine learning specialists and deep learning developers, SaaS provides access to powerful computing resources and servers for machine learning for training complex models.
Cloud services frequently include development platforms that support different machine learning frameworks and help developers deploy and scale algorithms. The cloud delivery model ensures that these resources are available on demand, providing the flexibility to use more or less computing power as a project requires.
Healthcare
SaaS providers in healthcare offer apps for patient records, appointment scheduling, and AI-driven diagnosis support.
These SaaS solutions follow strict cloud security and privacy rules to safeguard customer data.
Financial sector
In the financial sector, SaaS providers deliver business applications that can handle the entire procedure – from risk assessment to transaction processing. These SaaS solutions are designed with advanced security features to protect against fraud and ensure regulatory compliance.
Cloud computing services also provide the necessary data management tools to handle the vast amounts of financial data processed daily.
Education
The education sector also benefits from SaaS providers’ learning management systems (LMS) and virtual classrooms.
These applications enable institutions to offer online courses, track student progress, and integrate multimedia resources into their curricula, all accessible via web browsers.
HR Application
SaaS has also made significant progress in human resources with SaaS solutions that manage recruitment, onboarding, and employee performance.
These systems often include access management features, ensuring that sensitive employee information is kept secure.
Strategic Advancements in SaaS: Integration, Collaboration, and Security Insights
For cloud service providers, offering SaaS solutions means delivering SaaS products and ensuring their integration with existing traditional software. That is where the cloud service provider expertise comes into play – they can help you integrate SaaS applications with your business’s current systems and create a seamless workflow.
More and more SaaS companies are partnering with cloud providers like Microsoft Azure to utilize their cloud computing infrastructure. This helps SaaS companies enhance their customer service and grow their businesses. This partnership also ensures reliable and scalable SaaS apps, which is crucial if you rely on them for essential business operations.
As SaaS market trends evolve, we see a rise in IaaS SaaS providers (Infrastructure as a Service combined with Software as a Service), where you can leverage both the software and the underlying infrastructure from a third-party cloud provider. This new model enables more flexibility and scalability, letting you customize cloud services to your needs.
We moved from on-premise software solutions usage to cloud-based services, particularly SaaS models. This shift brings us greater flexibility and scalability but also introduces some challenges, particularly in SaaS security. SaaS providers should prioritize strong security measures, as SaaS software deals with online data storage and management. Meanwhile, to use SaaS to its full potential, users need to balance the convenience of cloud services with safeguarding sensitive information from cyber threats.
Overall, industry-specific SaaS applications are transforming the way organizations operate by providing specialized software tools that are accessible, scalable, and secure. Ongoing innovations in SaaS will increase their significance for industry operations, leading to improved efficiency and fresh business approaches.
Future Trends in SaaS
The SaaS industry is continually evolving, with new trends shaping the future of cloud computing and business software. As SaaS companies progress, they adapt to changing user demands, technological advancements, and cloud market trends.
We expect several significant trends to impact the SaaS model, providing new opportunities for growth and development.
AI and SaaS
One such trend is the increasing use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning within SaaS applications. SaaS providers are integrating these technologies to offer more intelligent and adaptive solutions. This integration allows you to perform advanced data analysis, predictive modeling, and automating tasks, enhancing SaaS capabilities.
Vertical SaaS
Another trend is the rise of vertical SaaS—it is becoming more popular as it serves niche industries or sectors. These vertical SaaS apps cater to specific markets’ unique needs, offering more specialized features than typical horizontal SaaS services. The demand for such targeted SaaS solutions will grow with the digitalization of industries.
Cloud Security
The importance of cloud security is also becoming more pronounced as businesses increasingly rely on SaaS vendors to handle sensitive data. SaaS providers are expected to continue investing in advanced security measures, including end-to-end encryption and robust access controls, to protect customer data and maintain compliance with evolving regulations.
Interoperability and integration will remain critical as businesses seek to integrate SaaS applications with other cloud services and legacy systems. SaaS vendors will likely focus on developing application programming interfaces (APIs) and development tools that facilitate seamless connections between different software platforms.
Cloud security is becoming more important as companies increasingly rely on SaaS vendors to handle sensitive data. SaaS providers invest in advanced security measures, like end-to-end encryption and robust access controls, to protect customer data and comply with evolving regulations.
To accommodate the integration of SaaS with other cloud services and legacy systems, SaaS providers prioritize the development of application programming interfaces (APIs) and development tools that ensure smooth connectivity between different platforms.
Conclusion
The SaaS market is more likely to expand with more solutions like platform-as-a-service (PaaS) and infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS) as SaaS providers look to offer a more comprehensive suite of cloud services. This will enable you to access many cloud computing resources through a single service provider, simplifying the management of their IT needs.
The future of SaaS is bright, with numerous trends indicating a path toward more intelligent, secure, and specialized SaaS tools. As digital transformation continues to evolve, SaaS companies will play a crucial role in businesses worldwide.
Frequently Asked Questions:
-
What are the core concepts of SaaS?
The core concepts of SaaS include centralized hosting, multi-tenancy, scalability, and accessibility, all with a focus on user experience and subscription-based pricing.
-
What are the key characteristics of successful SaaS solutions?
Successful SaaS solutions are reliable, secure, customizable, and offer excellent customer support, with the ability to integrate with other business applications.
-
What are the advantages of SaaS for businesses?
SaaS offers businesses cost savings, scalability, enhanced collaboration, advanced security, and access to the latest software without requiring infrastructure management.
-
What are the future trends in SaaS?
Future trends in SaaS include the integration of AI and machine learning, the rise of vertical SaaS, an increased focus on cloud security and interoperability, and the convergence of SaaS with PaaS and IaaS.