Cloud computing provides flexibility, scalability and efficiency for modern businesses and technologies. It’s a phrase covering various internet-delivered services, enabling users to access computing power effortlessly.
This idea has transformed how businesses function, letting them concentrate on core activities. For 3D design, animation, and architecture experts, cloud computing offers new creative possibilities.
As we explore cloud computing, it’s crucial to grasp its definition, workings, services, benefits, and drawbacks. This in-depth study benefits professionals like 3D designers, architects, and machine learning specialists.
What is Cloud Computing?
At its essence, cloud computing refers to providing services via the Internet. These services encompass tools such as data storage, servers, databases, networking, and software. Instead of storing files on a private hard drive, cloud storage allows for remotely saving files. Any device with internet access can access the data.
Cloud computing significantly changes how businesses view IT resources, reducing costs rapidly. Businesses can use compute resources as utilities, similar to electricity, without maintaining in-house infrastructures.
How Cloud Computing Works

Understanding how cloud computing works is important for professionals who depend on its reliability and power for their computing-intensive tasks. The basic structure of cloud computing involves a global network of physical servers in data centers.
These servers support cloud services by offering significant computing power for efficiently processing vast amounts of data. Cloud computing usually uses virtualization to allocate resources dynamically, dividing a physical hardware device into multiple virtual ones for computing tasks.
Virtualization allows cloud providers to offer a scalable computing model, adjusting resources based on demand. This flexibility, known as elasticity, is a defining feature of cloud computing. When utilizing the cloud, users access a network of virtualized resources managed by software that enables application installation and operation similar to a personal computer.
Multiple cloud computing services are provided online, offering broad network access to users through various devices. Computing occurs on remote servers in the cloud, accessed by users via the Internet. This setup enables multi-cloud and hybrid cloud strategies for businesses to customize their IT infrastructure.
Security is crucial in cloud computing, protecting sensitive data and critical applications. Providers focus on encryption, firewalls, and authentication to ensure data security and privacy. Another vital aspect is the cloud computing deployment models, which determine how services are provided.
The main models include public cloud, private cloud, and hybrid cloud. Public cloud services are managed by third-party providers and offer resources over the Internet. Private cloud services are solely for one entity, either on-site or hosted externally. Hybrid clouds merge public and private clouds, enabling data and app sharing.
Benefits for Businesses
Cloud computing allows businesses and individuals to access applications without installation and access personal files from any internet-connected computer. This technology centralized data storage, processing, and bandwidth for more efficient computing.
Also, it significantly benefits businesses needing high availability, scalability, and flexible computing power. It fosters collaboration among geographically dispersed teams, which is essential for remote work and global operations.
In our target group, like 3D designers and architects, cloud computing offers a way to use advanced software and manage complex tasks without relying on powerful local hardware. This levels the playing field for accessing top-notch computing power, enabling experts to concentrate on their strengths and creativity instead of dealing with IT systems.
Types of Cloud Services and Deploying Models
The types of cloud computing services are categorized into three main models, each serving a different purpose and offering various levels of control, flexibility, and management.
Below, we will review each one in more detail.
Software as a Service (SAAS)
Software as a service, or SAAS, involves hosting applications online by a service provider. It eliminates the need for organizations to install and operate applications.
This model transfers the provider’s responsibility of managing software, hardware, and provisioning. Users typically access SAAS applications through a web browser. For our target audience, SAAS covers email, communication tools, and software for 3D artists.
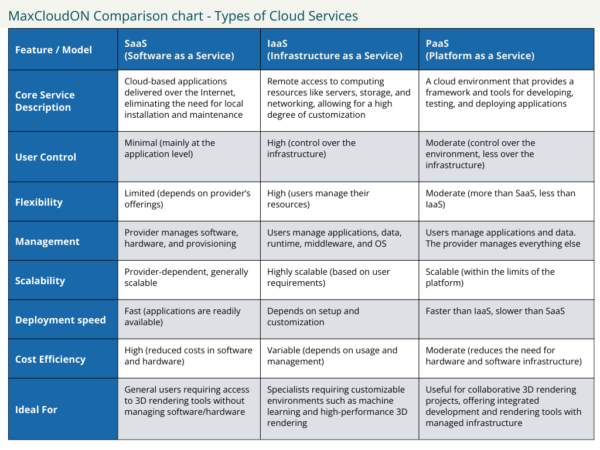
Infrastructure as a Service (IAAS)
Infrastructure as a service, or IAAS, offers virtualized computing infrastructure over the Internet. In this setup, a cloud provider hosts physical servers and infrastructure components usually found in an on-premises data center. These include servers, storage, and networking hardware, along with the virtualization or hypervisor layer.
Compared to other models, IAAS provides users with excellent flexibility and control over their cloud resources. It’s particularly beneficial for machine learning experts and deep learning developers requiring customizable environments for compute-heavy tasks.
Platform as a Service (PAAS)
Platform as a service, or PAAS, offers a complete platform for developing, running, and managing applications. PAAS simplifies workflows for multiple developers and external parties. It also aids architects and animation studios in creating custom project tools.
Each cloud service model provides varying levels of control, flexibility, and management tailored to specific requirements. For example, a business may opt for a multi-cloud or hybrid cloud strategy to optimize efficiency and performance.
Cloud Computing Advantages and Disadvantages
While the benefits of cloud computing architecture are numerous, it’s also important to consider the potential drawbacks. A comprehensive understanding of both can help businesses and professionals about implementing cloud solutions.
Learn more about this in the next section.
Advantages of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing offers game-changing benefits for different sectors, including scalability, customization, and accessibility. This allows 3D designers and animators to adjust rendering power as needed, eliminating hefty upfront investments.
Other advantages are the following ones:
- Cost savings: Businesses can avoid the upfront cost and complexity of owning and maintaining their IT infrastructure. Instead, they pay for what they use when they use it. This can result in significant cost reductions and operational efficiencies.
- Broad network access: services on various devices via the Internet. This benefits professionals collaborating with remote teams or clients.
Another pro is disaster recovery. Cloud computing offers disaster recovery and business continuity, which is challenging with on-premises IT. Data is backed up in the cloud and mirrored across redundant sites for availability.
Disadvantages of Cloud Computing
Despite its numerous benefits, cloud computing presents challenges and drawbacks. Security is a significant worry due to data storage on remote servers, posing risks of unauthorized access and breaches, especially for sensitive business data.
See some of the other cons below:
- Service outages: Cloud computing relies on internet connectivity, and if the service provider experiences an outage, this can lead to business disruptions. Additionally, physical data centers hosting the cloud services could be affected by natural disasters, impacting service availability.
- Restricted control and flexibility: While cloud providers handle the computing infrastructure, customers may have limited control over changes or updates.
- Vendor lock-in: Switching cloud service providers can be complicated and costly, as exporting large amounts of data can be time-consuming and may lead to compatibility issues.
Cloud computing offers various valuable services and models for businesses and professionals. Assessing pros and cons is vital to match the selected cloud solution with organizational requirements, objectives, and risk tolerance.
How Cloud Computing Can Help Your Business
Cloud computing is crucial in business, providing numerous benefits for operations, innovation, and growth.
Its flexible, scalable framework meets evolving business needs, offering essential computing capabilities without hardware management.
Enhancing Computing Capabilities
Cloud computing provides access to specialized hardware and computing power for companies needing powerful computing. Businesses can conduct complex computations and analyses through cloud services without hefty server investments. This is advantageous for small businesses needing more resources for extensive computing infrastructure.
Also, it enables serverless computing, where developers can build and run applications and services without managing the infrastructure. This model abstracts the server layer, allowing professionals to focus solely on their applications’ code and business logic.
For deep learning developers and machine learning specialists, this means they can deploy models and algorithms swiftly without worrying about the underlying system administration.
Cost-Effective Infrastructure Management
One main advantage of cloud computing is the cost savings linked to cloud infrastructure. Businesses can use resources from cloud service providers on a pay-as-you-go basis, avoiding initial investments and reducing overall ownership costs. The cloud provider manages infrastructure maintenance and updates, lowering business costs and workload.
Cloud computing provides extensive network access for deploying applications and services on various devices and platforms. This guarantees access to tools and data from anywhere, boosting productivity and supporting remote work.
Agility and Innovation
Cloud computing promotes agility and innovation, equipping businesses to meet market demands swiftly. Rapid resource provisioning allows risk-free experimentation with new ideas and technologies. This agility is crucial in creative fields like animation and graphic design.
In addition to that, it supports innovation through various services and platforms for developing new products and services. For instance, Platform as a Service (PAAS) offers a complete development and deployment environment in the cloud.

Cloud Computing Use Cases
The practical applications of cloud computing are vast and varied, touching nearly every industry and sector.
By examining specific use cases, we can better understand how cloud computing is being utilized to drive efficiency, innovation, and growth.
3D Rendering and Animation
Cloud computing has revolutionized the world of 3D rendering and animation. Cloud render nodes allow artists and studios to process tasks far more efficiently than on local machines. This speeds up rendering and enables real-time changes, improving workflow and reducing time to market. Whether you’re using tools like Blender, V-Ray, or Octane Render, selecting the best 3D rendering software is essential to maximize the capabilities of cloud rendering solutions.
Furthermore, cloud services aid artists in real-time 3D rendering collaboration, irrespective of location. Cloud computing’s structure supports this collaborative environment by offering a centralized resource-sharing platform.
Machine Learning and Deep Learning
Cloud computing offers essential computing power and infrastructure for machine learning experts and deep learning developers. Its scalability allows quick allocation of additional resources as needed, which is crucial for training deep learning models that demand substantial computational resources for processing data.
Moreover, cloud computing enables machine learning and deep learning professionals to access specialized hardware, such as GPUs and TPUs, which are optimized for these workloads. This access to specialized hardware, combined with the flexibility of cloud resources, allows for faster experimentation and development of machine learning models.
Architectural Visualization and Simulation
Cloud computing benefits architects and simulation developers by enabling detailed visualizations and simulations. Using cloud render nodes and services, they can create high-quality visuals and run complex simulations.
With it, architects can share designs with clients and stakeholders, instantly improving communication. Secure cloud deployment models for sharing project data enable this collaboration.
Conclusion: Embracing the Cloud for Future Success
The exploration of what is cloud computing has shown a landscape full of opportunities for businesses and professionals. The cloud computing model has proven to be a robust framework that enhances computing capabilities and offers a strategic advantage in today’s digital economy.
For different professionals, the cloud is a powerful ally that provides access to dedicated graphics hardware and computing power necessary for their complex and compute-intensive tasks. The ability to scale resources on-demand, the flexibility to work from anywhere, and the collaborative possibilities inherent in cloud services are just a few reasons cloud computing is integral to their success.
However, it’s also important to acknowledge its security concerns and potential disadvantages. While providers continue to enhance their security measures, businesses must remain vigilant and proactive in protecting their sensitive data. Additionally, the potential for service outages and the challenges of vendor lock-in are considerations that require careful planning and management.
Ultimately, the decision to adopt cloud computing should be informed by a thorough understanding of its advantages and limitations. By carefully selecting the right mix of services and deployment models, businesses can harness the cloud’s full potential to drive innovation and maintain a competitive edge in their respective fields.
Sources:
- Amazon Web Services – What is Cloud Computing?
- Microsoft Azure – What is Cloud Computing?
- Google Cloud – What is Cloud Computing?
- IBM Cloud – Cloud Computing
- Oracle – What is Cloud Computing?
- Cisco – What is Cloud Computing?
- Red Hat – What is IAAS?
- Gartner – Infrastructure as a Service (IAAS)
- NVIDIA – GPU Cloud Computing
- Cloudflare – What is the Cloud?
Frequently Asked Questions:
-
How does cloud computing enhance remote work capabilities?
Cloud computing provides broad network access to resources and applications, enabling remote work by allowing employees to access work-related data and tools from anywhere with an internet connection.
-
What should businesses consider when choosing a cloud service provider?
Businesses should evaluate cloud service providers based on their security measures, compliance with industry standards, service level agreements (SLAs), cost, scalability, and specific services and cloud resources.
-
How can cloud computing be leveraged for 3D rendering and animation?
Cloud computing can be leveraged for 3D rendering and animation by using cloud render nodes and dedicated graphics hardware to process rendering tasks more efficiently, allowing for real-time collaboration and scalability.
-
What are the implications of cloud computing for machine learning and deep learning?
For machine learning and deep learning, cloud computing provides scalable computing power and access to specialized hardware, enabling the training of complex models and faster experimentation.